Her parents needed a Spanish-speaking doctor. She's becoming one to break down health care barriers.
By Genaro C. Armas, American Heart Association News
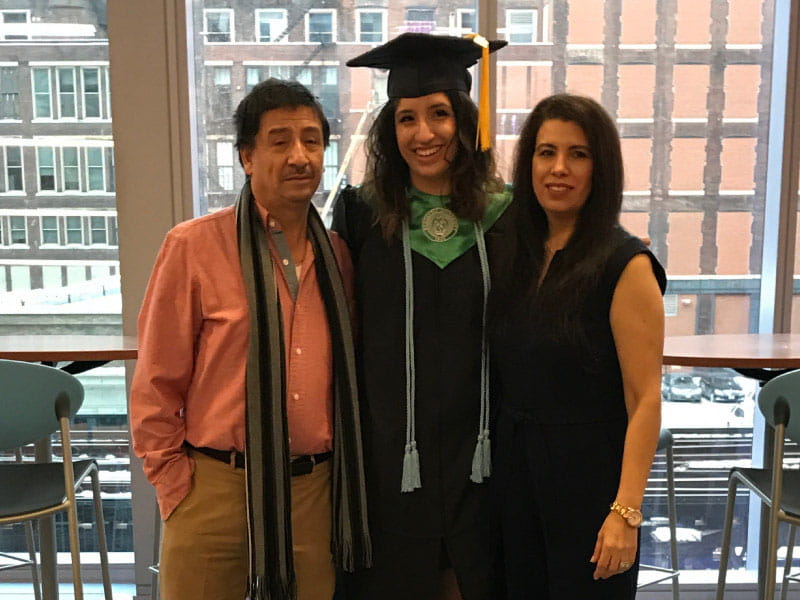

Immigrants from Mexico, her parents mainly spoke Spanish and had trouble finding Spanish-speaking doctors. Melissa would accompany her mother and father to medical visits to be their interpreter.
When it came time to apply for college, Melissa decided to pursue pre-med programs with a goal of becoming a doctor. Now, she is a third-year medical student at Universidad Autónoma de Guadalajara in Mexico, doing her clinical rotations back in Chicago.
She is committed to eradicating barriers to health care in the Latino community.
"Watching my parents struggle as they navigated the health care system is what made me realize there was a need for Spanish-speaking health care workers – especially for doctors," Melissa said. "This early exposure is what inspired me to become the doctor my parents needed back then."
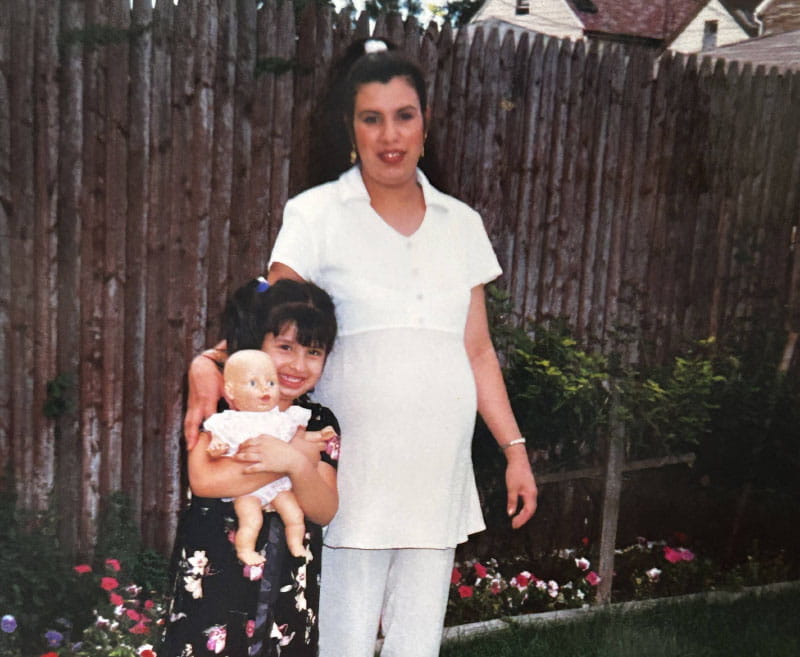
Spanish is the second-most commonly spoken language in the United States, with about 13% of the total population speaking the language at home, according to census data.
While survey data published last year in American Family Physician found that more than 22% of family physicians say they speak Spanish, there were "inadequate numbers" of Spanish-speaking family physicians in many U.S. counties where high proportions of the population speak the language. In fact, 222 counties where more than 20% of the population speaks Spanish had no Spanish-speaking family physicians.
Having one Spanish-speaking physician for every 1,500 people who speak the language in a community was considered an adequate ratio, according to the American Family Physician study. A cluster of communities in the Chicago area and northeastern Illinois had a ratio of more than 1,500-to-1.
"As the U.S. population continues to diversify, it is increasingly important to recruit Spanish-speaking medical students to serve Spanish-speaking populations and for Spanish to be taught in medical school and family medicine residency programs," the study's authors wrote.
Melissa witnessed how language barriers impacted people in her broader community. After attending Chicago's Roosevelt University, she worked as a medical assistant in a primary care clinic that needed her to interpret for Spanish-speaking patients.
She found that patients needed more than an interpreter. Melissa studied to become a certified diabetic educator to help patients manage diabetes and other chronic medical conditions.
"That's how my interest in cardiometabolic disease came about," she said. "I found it really fascinating, especially seeing how it affected people who looked like me and my family members."
Melissa chose to go to medical school in her mother's hometown of Guadalajara, in the western Mexican state of Jalisco. She started school in July 2020, and has had to weather the challenges that came with adjusting to a new home early in the COVID-19 pandemic.
She persevered. Now a third-year medical student, she has been named a scholar in the American Heart Association's National Hispanic Latino Cardiovascular Collaborative mentoring program.
The goal of the program is to engage with medical students through networking, mentorship and opportunities to grow and diversify the future health care workforce, promoting cardiovascular health for all populations.
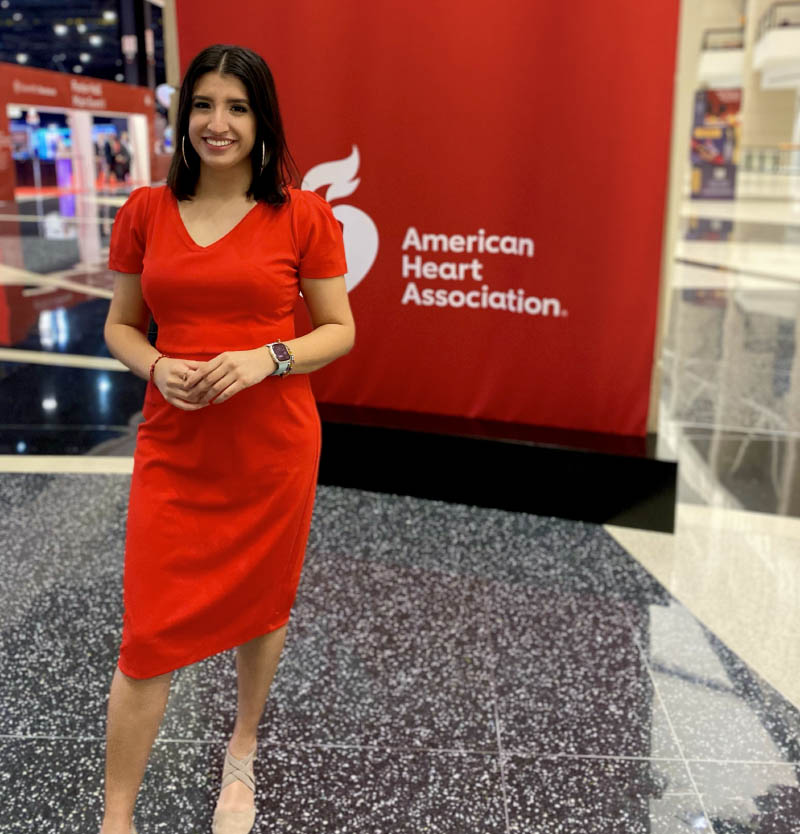

International medical school students aren't often represented in programs that allow them to connect with mentors as well as other aspiring doctors coming from medical schools outside the U.S., she said.
"And now, I'm fortunate enough to be back in Chicago for my clinical rotations, and I am able to bring this cultural sensitivity and advocacy not only for people of Mexican descent, but for all Latinos in the United States," she said. "It's truly an honor."
One of her first unofficial patients might be her biggest fan.
Her mother, Guillermina Rodríguez, recalled a recent trip to the hospital to have surgery. Melissa was by her side, as usual, guiding her parents through the process.
Not only is Melissa on track to become the first person in the family to become a doctor, she also is the first in the family to graduate from college. Her two younger sisters have also since graduated from college.
"I can tell that she does it well, and it's something that she's passionate about," a smiling Guillermina said about her daughter's pursuit of a medical career. "I cannot explain how proud I am of her."





